DIPHTHERIA
A highly contagious bacterial infection that spreads from person to person, often through respiratory droplets, like from coughing or sneezing. Globally, incidence of diphtheria is on the rise. Death occurs in 5% to 10% of those infected, mainly in children aged under five.
Explore article
TETANUS
A serious, life-threatening disease that affects the central nervous system and enters the body through wounds or cuts. Neonatal tetanus continues to be a major killer of newborns and can be prevented by providing the vaccine to women of childbearing age, either before or during pregnancy.
Explore article
PERTUSSIS (WHOOPING COUGH)
A highly contagious and serious respiratory disease that spreads easily from infected persons and is fatal in 1 in 200 cases among infants.
Explore article
HAEMOPHILUS INFLUENZAE TYPE B
A deadly bacterium that can cause meningitis, pneumonia and septicaemia – spread through sneezing and coughing. Hib is the third-leading vaccine-preventable cause of death in under-fives. In lower-income countries, where most Hib deaths occur, the disease leaves up to 35% of survivors with disabilities.
Explore article
HEPATITIS B
A viral infection that affects the liver and is transmitted by body fluids or the blood of infected people. HepB is the leading cause of liver cancer and is 50 times more infectious than HIV. Transmission of the virus from mother to newborn infant is a major contribution to disease in regions such as South-East Asia and the Western Pacific, where infection is widespread. Most cases could be avoided through vaccination.
Explore article
Gavi's response
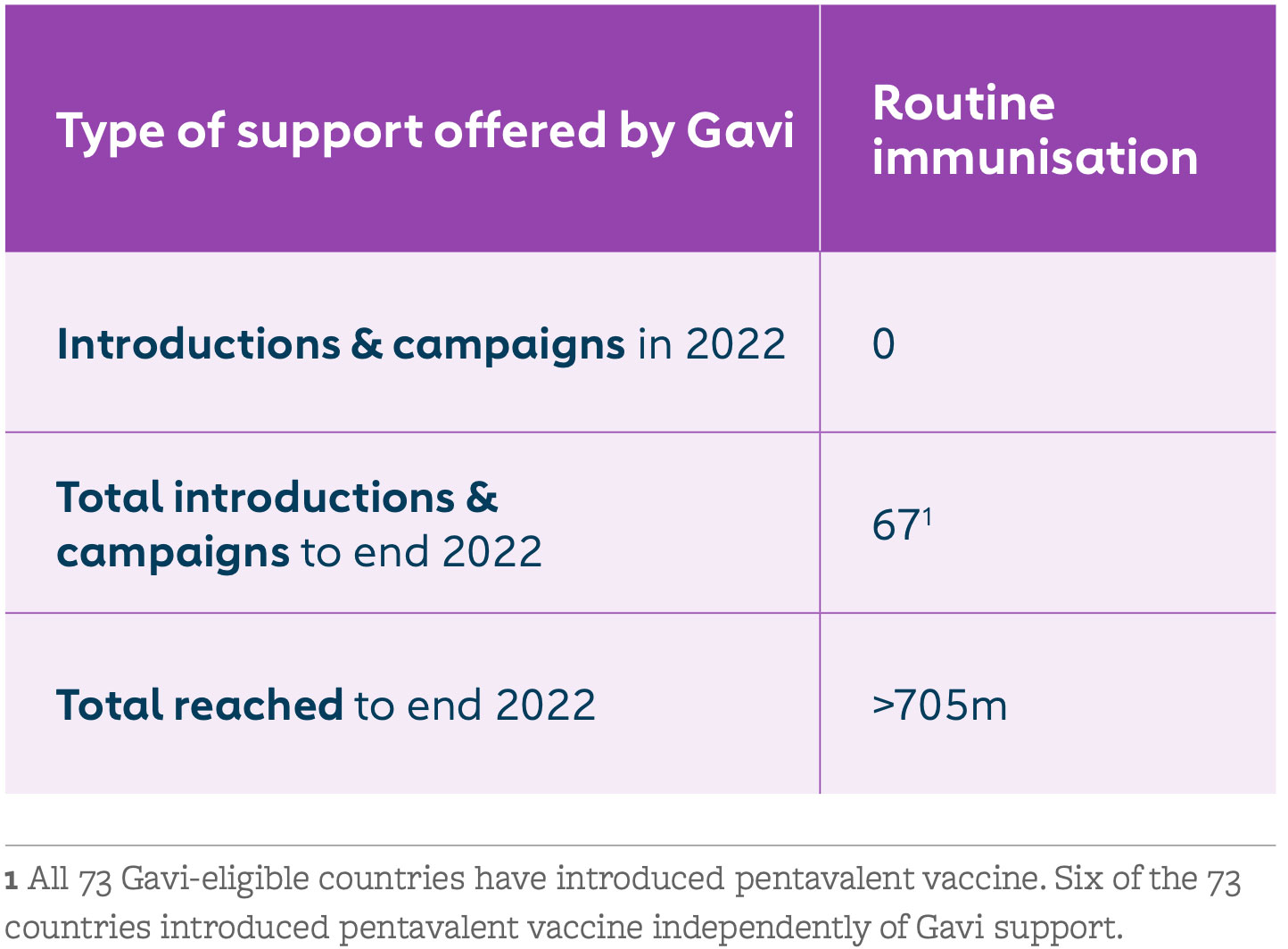
Gavi began supporting pentavalent vaccine in 2001. The goal was to boost the low uptake of Hib and hepB vaccines by making them part of routine immunisation programmes in low-income countries. Since 2012, Gavi has supported Hib and hepB vaccines only as part of the pentavalent vaccine. With our support, the pentavalent vaccine is now available in the world’s 73 lowest-income countries.
Countries have seen remarkable benefits from this combination vaccine, including cost savings, improved programmatic efficiencies, increased coverage and equity, and reduced environmental impact – among other advantages.
The pentavalent vaccine success story reflects the strengths of Gavi’s public-private partnership model. UNICEF Supply Division has met demand for over 1 billion doses; WHO and UNICEF helped countries decide when and how to introduce the vaccine; and industry has increased global production capacity from 20 to 600 million doses. At the same time, innovation in formulation and packaging has helped to reduce the strain on immunisation cold chains.
Starting 1 December 2023, countries eligible for Gavi support can apply to switch to a whole-cell pertussis (wP) hexavalent vaccine – a six-in-one vaccine that combines the pentavalent antigens with inactivated polio vaccine (IPV) – or continue using pentavalent and IPV standalone vaccines. At this time, eligible countries can also apply for support to introduce any of the three WHO-recommended DTP-containing vaccine boosters in the national immunisation schedule (12–23 months, 4–7 years and 9–15 years).
FROM OTHER SITES